Medical-grade glycolic peels have become a popular cosmetic treatment in the UK for individuals seeking to improve their skin’s texture, tone, and overall appearance. Glycolic peels are a type of chemical exfoliation that uses glycolic acid, an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) derived from sugarcane. Unlike over-the-counter skin care products, medical-grade peels are more potent and are administered by professionals in clinical settings. They can treat a variety of skin concerns, from fine lines and wrinkles to acne, hyperpigmentation, and uneven skin tone. This article provides an in-depth look at medical-grade glycolic peels, their benefits, the procedure, aftercare, risks, and why they are an effective treatment for improving skin health and aesthetics in the UK.
What is Glycolic Acid?
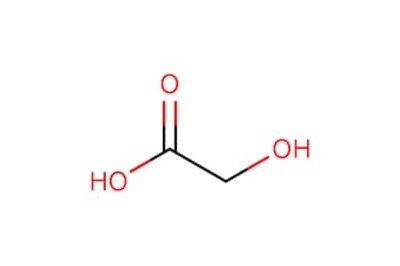
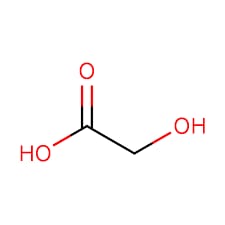 Glycolic acid is one of the most commonly used AHAs in skin care due to its small molecular size, which allows it to penetrate the skin effectively. This acid works by loosening the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, enabling them to be exfoliated more easily. As the dead cells are removed, fresh, younger-looking skin is revealed, and the overall appearance of the skin becomes smoother, brighter, and more even-toned.
Glycolic acid is one of the most commonly used AHAs in skin care due to its small molecular size, which allows it to penetrate the skin effectively. This acid works by loosening the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, enabling them to be exfoliated more easily. As the dead cells are removed, fresh, younger-looking skin is revealed, and the overall appearance of the skin becomes smoother, brighter, and more even-toned.
Medical-grade glycolic acid peels typically contain higher concentrations of glycolic acid than at-home products. Concentrations can range from 30% to 70%, depending on the patient’s skin type, concerns, and the desired outcome. Medical-grade peels are stronger and penetrate more deeply than superficial peels, making them highly effective at addressing deeper skin issues.
Benefits of Medical-Grade Glycolic Peels
Medical-grade glycolic peels offer a wide range of benefits for people with various skin types and concerns. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Exfoliation and Skin Renewal
 Glycolic acid peels provide deep exfoliation by breaking down the bonds between the cells of the outermost layer of the skin. This process promotes the shedding of dead skin cells, leading to a smoother and more refined skin surface. Regular exfoliation also helps unclog pores, prevent acne, and reduce the risk of breakouts.
Glycolic acid peels provide deep exfoliation by breaking down the bonds between the cells of the outermost layer of the skin. This process promotes the shedding of dead skin cells, leading to a smoother and more refined skin surface. Regular exfoliation also helps unclog pores, prevent acne, and reduce the risk of breakouts.
2. Improvement of Fine Lines and Wrinkles
Glycolic acid is known to stimulate the production of collagen, a protein that is essential for maintaining the skin’s elasticity and firmness. Over time, this stimulation can reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. The peel helps to thicken the epidermis, which becomes thinner as we age, thereby improving skin texture and making the skin look more youthful.
3. Brightening and Evening Out Skin Tone
Glycolic peels are particularly effective in treating hyperpigmentation, dark spots, and uneven skin tone. The exfoliating action helps to fade pigmentation caused by sun damage, acne scars, and melasma by removing the discolored skin cells and encouraging new, evenly pigmented cells to surface. Over time, patients often notice a brighter, more radiant complexion with fewer areas of discoloration.
4. Acne Treatment and Prevention
For individuals suffering from acne, medical-grade glycolic peels can be highly effective. Glycolic acid helps to clear clogged pores, reduce the formation of blackheads and whiteheads, and control excess oil production, which can contribute to acne. Additionally, glycolic acid’s anti-inflammatory properties can help to reduce redness and swelling associated with acne, promoting faster healing of active breakouts.
5. Reduction of Acne Scars
 In addition to treating active acne, glycolic peels can also help reduce the appearance of acne scars. The exfoliating action smooths out the skin’s surface, making shallow scars less noticeable. Over time, repeated treatments can improve the skin’s texture, leaving it more even and refined.
In addition to treating active acne, glycolic peels can also help reduce the appearance of acne scars. The exfoliating action smooths out the skin’s surface, making shallow scars less noticeable. Over time, repeated treatments can improve the skin’s texture, leaving it more even and refined.
6. Improvement in Hydration
Though glycolic acid is primarily known for its exfoliating properties, it also has hydrating effects. Glycolic acid helps the skin retain moisture by attracting water molecules to the skin’s surface, which can improve skin hydration and elasticity. This makes it an ideal treatment for individuals with dry or dehydrated skin.
7. Stimulation of Collagen Production
Collagen is a critical component of youthful skin, providing structure and firmness. Glycolic acid peels stimulate collagen production, which can help to improve skin elasticity, reduce sagging, and give the skin a plumper, firmer appearance. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals looking to address the early signs of aging.
The Procedure: What to Expect During a Medical-Grade Glycolic Peel
The procedure for a medical-grade glycolic peel is relatively simple and non-invasive, but it requires the expertise of a trained professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Here’s what to expect during the process:
1. Initial Consultation
Before undergoing a glycolic peel, patients typically have an initial consultation with a dermatologist or aesthetic practitioner. During this consultation, the practitioner will assess the patient’s skin type, discuss their skin concerns and goals, and determine the appropriate strength of glycolic acid for the peel. The practitioner may also review the patient’s medical history to ensure that the treatment is safe for them. Please see my blog ‘The importance of finding the right aesthetics practitioner’
2. Pre-Treatment Skin Preparation
In some cases, patients may be asked to prepare their skin for the peel by using specific skincare products in the weeks leading up to the treatment. This may include using a lower-strength glycolic acid cleanser or retinoid to help prime the skin and enhance the results of the peel.
3. Cleansing and Preparation
On the day of the peel, the practitioner will cleanse the skin to remove any dirt, oil, and makeup. This step ensures that the peel is applied to clean, bare skin, allowing for better penetration.
4. Application of Glycolic Acid
The glycolic acid solution is applied to the skin using a brush or cotton pad. The practitioner carefully monitors the skin’s response to the acid, ensuring that it is evenly applied and that the patient is comfortable. Depending on the strength of the peel and the patient’s skin type, the glycolic acid may be left on the skin for anywhere from 2 to 10 minutes.
5. Neutralization and Removal
After the glycolic acid has been on the skin for the desired amount of time, the practitioner will neutralize the peel using a special solution. This step stops the action of the acid and prevents it from penetrating deeper layers of the skin. The neutralized peel is then gently removed.
6. Post-Peel Care
Following the procedure, the skin may feel tight and slightly sensitive. The practitioner will apply a soothing moisturizer and sunscreen to protect the skin. Patients are also given post-treatment care instructions to ensure optimal healing and results.
Aftercare and Recovery
While medical-grade glycolic peels typically require minimal downtime, patients need to follow specific aftercare guidelines to ensure proper healing and avoid complications. Some common post-peel instructions include:
- Avoid Sun Exposure: After a glycolic peel, the skin is more sensitive to UV radiation. Patients should avoid direct sun exposure and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 daily.
- Moisturize: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential after a peel. Patients should use a gentle, hydrating moisturizer to soothe the skin and promote healing.
- Avoid Harsh Skincare Products: In the days following the peel, patients should avoid using exfoliants, retinoids, and other harsh skincare products that could irritate the skin.
- Expect Mild Peeling: Some mild peeling or flaking of the skin is normal after a glycolic peel, especially with higher concentrations. Patients should avoid picking at the peeling skin to prevent irritation or scarring.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and keeping the skin hydrated is crucial during the healing process.
Risks and Side Effects
While medical-grade glycolic peels are generally safe when performed by qualified professionals, there are some potential risks and side effects, especially if the peel is not administered correctly or if aftercare instructions are not followed. Common side effects include:
- Redness and Sensitivity: It is normal for the skin to be slightly red and sensitive immediately after the peel. This should subside within a few days.
- Peeling and Flaking: As the skin sheds its outer layer, some peeling or flaking may occur. This is a sign that the peel is working, but it’s important not to pick at the skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: In rare cases, patients may experience post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially if they do not protect their skin from the sun after the peel.
- Infection: Though rare, infections can occur if the skin is not properly cared for after the peel. Patients should follow all post-treatment instructions to reduce this risk.
Why Medical-Grade Peels?
The primary distinction between medical-grade glycolic peels and those available over-the-counter is the concentration of glycolic acid and the depth of penetration. Medical-grade peels, which are administered by licensed professionals, offer stronger exfoliation and can address more severe skin concerns. They provide longer-lasting and more dramatic results than at-home peels, making them a popular choice for individuals looking to rejuvenate their skin with minimal downtime.
Conclusion
Medical-grade glycolic peels offer an effective solution for those seeking to improve their skin’s texture, tone, and overall appearance. By exfoliating the skin, stimulating collagen production, and addressing concerns such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and wrinkles, glycolic peels can deliver noticeable results after just a few sessions. However, because of the strength of these peels, it’s important to choose a qualified practitioner who can tailor the treatment to your specific skin needs and ensure a safe and effective outcome. With proper care and maintenance, glycolic peels can be a transformative addition to your skincare routine, offering smoother, brighter, and more youthful-looking skin.