In the pursuit of healthy, glowing skin, many focus on cleansers, serums, and moisturizers, often overlooking one of the most critical steps in skincare: sunscreen. A good quality SPF (sun protection factor) is not just an optional add-on but a fundamental part of any effective daily skincare routine. Whether you’re preventing premature aging, protecting against hyperpigmentation, or reducing the risk of skin cancer, incorporating SPF into your regimen is non-negotiable. This article explores why a high-quality SPF is essential, how it benefits your skin, and how to choose the best product to suit your needs.
What Is SPF?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor, and it measures a sunscreen’s ability to shield your skin from ultraviolet B (UVB) rays, the type responsible for sunburn and contributing significantly to skin cancer.
- SPF 30 filters out approximately 97% of UVB rays.
- SPF 50 blocks about 98% of UVB rays.
While the difference between these levels may seem minimal, every percentage counts when it comes to protecting your skin from cumulative sun damage.
Broad-spectrum sunscreens also guard against UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin. These rays are the culprits behind premature aging, collagen breakdown, and hyperpigmentation. A good quality SPF ensures protection from both UVA and UVB, safeguarding your skin comprehensively.
Why SPF Is Crucial for Daily Use
1. Protection Against Skin Cancer
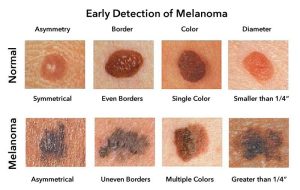 Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers in the UK and worldwide. Overexposure to UV radiation is the primary cause of both melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers. The British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) highlights that using sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days, can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers in the UK and worldwide. Overexposure to UV radiation is the primary cause of both melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers. The British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) highlights that using sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days, can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer.
2. Prevention of Premature Aging
Up to 80% of visible aging is caused by sun exposure. UVA rays penetrate deep into the dermis, breaking down collagen and elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin. A quality SPF acts as a barrier, preventing these rays from causing damage and preserving the skin’s youthful appearance.
3. Reduction of Hyperpigmentation
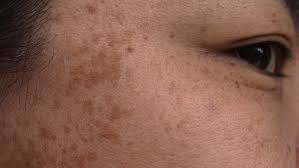 Hyperpigmentation, including melasma, dark spots, and post-inflammatory marks from acne, is often worsened by sun exposure. UV rays stimulate melanocytes (the cells that produce pigment), exacerbating discoloration. Regular use of a high-quality SPF prevents these effects, allowing the skin to maintain an even tone.
Hyperpigmentation, including melasma, dark spots, and post-inflammatory marks from acne, is often worsened by sun exposure. UV rays stimulate melanocytes (the cells that produce pigment), exacerbating discoloration. Regular use of a high-quality SPF prevents these effects, allowing the skin to maintain an even tone.
4. Protection from Photosensitivity
Certain medications (e.g., antibiotics or acne treatments) and skincare ingredients (like retinol and AHAs) make the skin more sensitive to sunlight. Without SPF, this increased sensitivity can lead to severe burns or irritation.
5. Maintaining Skin Health
UV damage causes inflammation and oxidative stress, compromising the skin’s barrier function. A compromised barrier can lead to dryness, redness, and irritation. SPF helps to maintain the skin’s natural defenses, keeping it healthy and hydrated.
What Makes a Good Quality SPF?
Not all sunscreens are created equal. A good quality SPF will offer the following:
1. Broad-Spectrum Protection
Look for sunscreens labeled as “broad-spectrum,” meaning they protect against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA protection is crucial for preventing premature aging, while UVB protection guards against burning and skin cancer.
2. SPF Rating of 30 or Higher
While SPF 15 offers basic protection, SPF 30 or higher is recommended for daily use. If you spend extended time outdoors, SPF 50 is a safer choice.
3. Non-Comedogenic Formula
For those prone to acne or clogged pores, a non-comedogenic sunscreen is essential. These formulas do not block pores and are less likely to cause breakouts.
4. Water Resistance
If you plan to swim, exercise, or sweat, choose a water-resistant sunscreen to ensure consistent protection. However, reapplication after swimming or sweating is still necessary.
5. Additional Skin Benefits
Modern sunscreens often include added benefits, such as antioxidants (to combat free radical damage), moisturizing agents (to hydrate the skin), or a tint for natural coverage.
How to Incorporate SPF into Your Skincare Routine
SPF should be the final step in your morning skincare regimen, applied after moisturizers and serums but before makeup.
- Cleanse: Start with a gentle cleanser to remove impurities.
- Treat: Apply serums or treatments like Vitamin C, which pairs well with SPF to enhance protection.
- Moisturize: Hydrate your skin to create a smooth base.
- Apply SPF: Use a generous amount—about a teaspoon for the face and neck.
Reapply every two hours when outdoors, especially if exposed to direct sunlight, swimming, or sweating.
Common Myths About SPF
“I only need SPF in summer.”
UV rays are present year-round, even on cloudy days or during winter. UVA rays, in particular, can penetrate clouds and windows, making daily protection vital.
“Dark skin doesn’t need sunscreen.”
While melanin provides some natural protection, it is not sufficient to prevent skin cancer or aging. Individuals of all skin tones benefit from daily SPF use.
“Makeup with SPF is enough.”
Most makeup with SPF does not provide adequate protection, as the amount applied is typically far less than required. A dedicated sunscreen is essential.
Choosing the Right SPF for Your Skin Type
1. Oily or Acne-Prone Skin
Opt for lightweight, oil-free formulas with a matte finish. Gel or water-based sunscreens are excellent choices.
2. Dry Skin
Choose sunscreens with hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid or glycerin to prevent dryness.
3. Sensitive Skin
Mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are less likely to cause irritation. Avoid fragrances and harsh chemicals.
4. Aging Skin
Look for sunscreens that include antioxidants, peptides, or ceramides to target aging concerns while protecting against UV damage.
Environmental and Lifestyle Considerations
Pollution
Urban environments expose the skin to pollution, which can amplify the effects of UV radiation. Antioxidant-enriched sunscreens provide an extra layer of defense.
High Altitudes
UV exposure increases at higher altitudes, making sunscreen crucial for activities like hiking or skiing.
Reflection from Surfaces
Water, sand, and snow reflect sunlight, increasing UV exposure. Always reapply sunscreen in these conditions.
Tips for Maximizing Sunscreen Effectiveness
- Apply Generously: Use about two fingers’ worth of sunscreen for the face and neck.
- Reapply Regularly: Sunscreen wears off throughout the day, so reapply every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.
- Don’t Forget Vulnerable Areas: Apply sunscreen to often-overlooked spots like the ears, scalp, lips, and hands.
- Pair with Other Protective Measures: Use hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing alongside sunscreen for comprehensive protection.
The Role of SPF in Long-Term Skin Health
Daily use of a good quality SPF not only protects against immediate damage like sunburn but also plays a critical role in maintaining skin health over time. By preventing collagen breakdown, reducing the risk of skin cancer, and maintaining an even complexion, sunscreen helps to preserve your skin’s integrity and appearance well into the future.
Conclusion
A good quality SPF is more than just a skincare product—it is a daily necessity for anyone serious about skin health. By protecting against UV damage, preventing premature aging, and reducing the risk of skin cancer, sunscreen is the cornerstone of any effective skincare routine.
Whether you are young or old, fair-skinned or dark, indoors or outdoors, incorporating SPF into your daily regimen is one of the simplest yet most impactful ways to ensure your skin remains healthy, radiant, and resilient for years to come. Make SPF a priority, and your skin will thank you.